Problem description
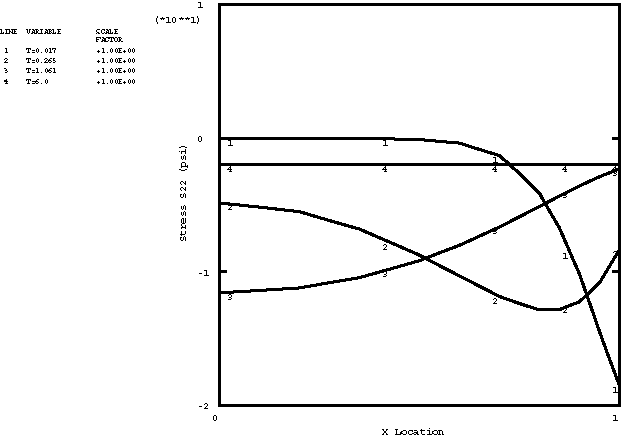
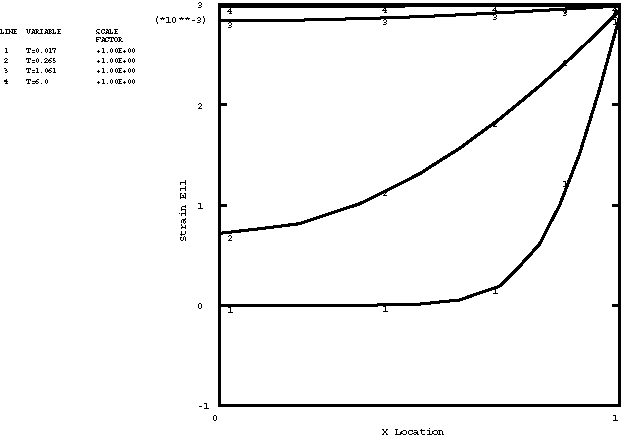
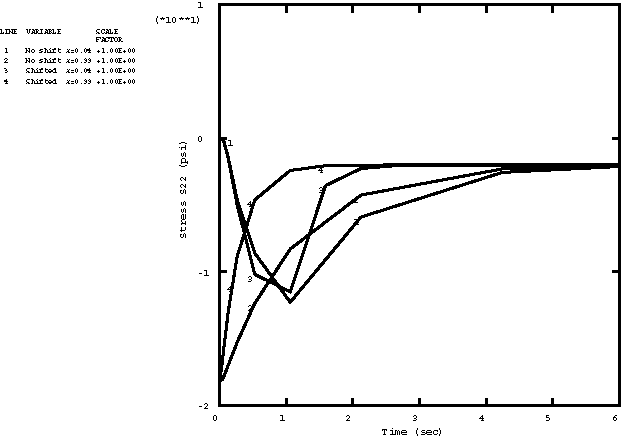
The example, taken from Collingwood et al. (1985), models a viscoelastic slab under plane strain restrained in all directions in its plane and examines the response of the slab after the temperature of its faces is raised suddenly to 100°.
The slab has unit half-thickness. Since the problem is one-dimensional, the slab is modeled with a single row of plane strain continuum elements. In Abaqus/Standard a sequential thermal-stress analysis is performed with two-dimensional, 8-node heat transfer elements, DC2D8, used for the heat transfer analysis and the corresponding 8-node plane strain continuum elements, CPE8R, used for the stress analysis. The mesh is shown in Figure 1. In Abaqus/Explicit a coupled thermal-stress analysis is performed using first-order plane strain elements (CPE3T and CPE4RT) to model the slab. Twenty elements are used along the length of the slab in the Abaqus/Explicit simulation.
The initial temperature throughout the slab is 0°. The outside face of the slab, at 1, is instantaneously raised to 100°. The mesh (Figure 1) is finer toward 1, where the temperature gradient is expected to be highest. The resulting transient temperature distribution is written to the results file and used as input to the subsequent stress analysis. Plane strain is imposed in the Y-direction by setting 0 on the two faces of the mesh at 0 and 1. Symmetry about 0 is also imposed.