Energy Dissipation in Elastomeric Foams
Abaqus provides a mechanism to include permanent energy dissipation and stress softening effects in elastomeric foams. The approach is similar to that used to model the Mullins effect in elastomeric rubbers, described in Mullins Effect. The functionality is primarily intended for modeling energy absorption in foam components subjected to dynamic loading under deformation rates that are high compared to the characteristic relaxation time of the foam; in such cases it is acceptable to assume that the foam material is damaged permanently.
The material response is depicted qualitatively in Figure 1.
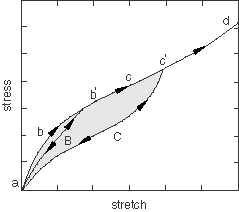
Consider the primary loading path of a previously unstressed foam, with loading to an arbitrary point . On unloading from , the path is followed. When the material is loaded again, the softened path is retraced as . If further loading is then applied, the path is followed, where is a continuation of the primary loading path (which is the path that would be followed if there were no unloading). If loading is now stopped at , the path is followed on unloading and then retraced back to on reloading. If no further loading beyond is applied, the curve represents the subsequent material response, which is then elastic. For loading beyond , the primary path is again followed and the pattern described is repeated. The shaded area in Figure 1 represents the energy dissipated by damage in the material for deformation until .
Modified Strain Energy Density Function
Energy dissipation effects are accounted for by introducing an augmented strain energy density function of the form
where represent the principal mechanical stretches and is the strain energy potential for the primary foam behavior described in Hyperelastic Behavior in Elastomeric Foams, defined by the polynomial strain energy function
The function is a continuous function of the damage variable, , and is referred to as the “damage function.” The damage variable varies continuously during the course of the deformation and always satisfies , with on the points of the primary curve. The damage function satisfies the condition ; thus, when the deformation state of the material is on a point on the curve that represents the primary foam behavior, and the augmented energy function reduces to the strain energy potential for the primary foam behavior.
The above expression of the augmented strain energy density function is similar to the form proposed by Ogden and Roxburgh to model the Mullins effect in filled rubber elastomers (see Mullins Effect), with the difference that in the case of elastomeric foams an augmentation of the total strain energy (including the volumetric part) is considered. This modification is required for the model to predict energy absorption under pure hydrostatic loading of the foam.
Stress Computation
With the above modification to the energy function, the stresses are given by
where is the stress corresponding to the primary foam behavior at the current deformation level . Thus, the stress is obtained by simply scaling the stress of the primary foam behavior by the damage variable, . From any given strain level the model predicts unloading/reloading along a single curve (that is different, in general, from the primary foam behavior) that passes through the origin of the stress-strain plot. The model also predicts energy dissipation under purely volumetric deformation.
Damage Variable
The damage variable, , varies with the deformation according to
where is the maximum value of at a material point during its deformation history; r, , and m are material parameters; and is the error function. When , corresponding to a point on the primary curve, . On the other hand, upon removal of deformation, when , the damage variable, , attains its minimum value, , given by
For all intermediate values of , varies monotonically between and . While the parameters r and are dimensionless, the parameter m has the dimensions of energy. The material parameters can be specified directly or can be computed by Abaqus based on curve fitting of unloading-reloading test data. These parameters are subject to the restrictions , , and (the parameters and m cannot both be zero). Alternatively, the damage variable can be defined through user subroutine UMULLINS in Abaqus/Standard and VUMULLINS in Abaqus/Explicit.
If the parameter and the parameter m has a value that is small compared to , the slope of the stress-strain curve at the initiation of unloading from relatively large strain levels might become very high. As a result, the response might become discontinuous. This kind of behavior might lead to convergence problems in Abaqus/Standard. In Abaqus/Explicit the high stiffness will lead to very small stable time increments, thereby leading to a degradation in performance. This problem can be avoided by choosing a small value for . In Abaqus/Standard the default value of is 0. In Abaqus/Explicit, however, the default value of is 0.1. Thus, if you do not specify a value for , it is assumed to be 0 in Abaqus/Standard and 0.1 in Abaqus/Explicit.
The parameters r, , and m do not have direct physical interpretations in general. The parameter m controls whether damage occurs at low strain levels. If , there is a significant amount of damage at low strain levels. On the other hand, a nonzero m leads to little or no damage at low strain levels. For further discussion regarding the implications of this model on the energy dissipation, see Mullins effect.
Specifying Properties for Energy Dissipation in Elastomeric Foams
The primary elastomeric foam behavior is defined by using the hyperfoam material model. Energy dissipation can be defined by specifying the parameters in the expression of the damage variable directly or by using test data to calibrate the parameters. Alternatively, you can define the Mullins effect model with user subroutine UMULLINS in Abaqus/Standard and VUMULLINS in Abaqus/Explicit.
Specifying the Parameters Directly
The parameters r, m, and in the expression of the damage variable can be given directly as functions of temperature and/or field variables.
Input File Usage
MULLINS EFFECT
Abaqus/CAE Usage
Property module: material editor: : Definition: Constants
Using Test Data to Calibrate the Parameters
Experimental unloading-reloading data from different strain levels can be specified for up to three simple tests: uniaxial, biaxial, and planar. Abaqus will then compute the material parameters using a nonlinear least-squares curve fitting algorithm. See Mullins Effect for a detailed discussion of this approach.
Input File Usage
MULLINS EFFECT, TEST DATA INPUT, BETA and/or M and/or R
In addition, use at least one and up to three of the following options to give the unloading-reloading test data:
UNIAXIAL TEST DATA BIAXIAL TEST DATA PLANAR TEST DATA
Multiple unloading-reloading curves from different strain levels for any given test type can be entered by repeated specification of the appropriate test data option.
Abaqus/CAE Usage
Property module: material editor: : Definition: Test Data Input: enter the values for up to two of the values r, m, and beta. In addition, enter data for at least one of the following , , or
User Subroutine Specification
An alternative method for specifying energy dissipation involves defining the damage variable in user subroutine UMULLINS in Abaqus/Standard and VUMULLINS in Abaqus/Explicit. Optionally, you can specify the number of property values needed as data in the user subroutine. You must provide the damage variable, , and its derivative, . The latter contributes to the Jacobian of the overall system of equations and is necessary to ensure good convergence characteristics in Abaqus/Standard. If needed, you can specify the number of solution-dependent variables (About User Subroutines and Utilities). These solution-dependent variables can be updated in the user subroutine. The damage dissipation energy and the recoverable part of the energy can also be defined for output purposes.
Input File Usage
MULLINS EFFECT, USER, PROPERTIES=constants
Abaqus/CAE Usage
Property module: material editor: : Definition: User Defined