-
When creating a mapped field from an output database, you must have
two files open and displayed simultaneously in separate viewports:
-
the model database (.cae) file containing
your main target model for the mapping, and
-
the output database (.odb) file containing
field output variable data from a previous analysis run on the same (or
similar) model.
-
Select the source data you want to use.
-
In
the Visualization module,
open the output database file that contains the source data.
-
Display the undeformed contour plot in a viewport. You can also
use the deformed plot, but the data are still read from the undeformed mesh.
-
Choose the field output variable for the values you want to map,
at a specific step and frame of the analysis. See
Producing a contour plot,
for details about contour plots.
-
In the model database containing the main (target) model, open the
Create Mapped Field dialog box using one of the following
methods:
-
From the main menu bar, select
.
-
From the interaction editor in the
Interaction module,
click
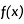 next to the Definition or
Emissivity distribution field.
next to the Definition or
Emissivity distribution field.
-
From the load, boundary condition, or predefined field editor in
the
Load module,
click
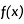 next to the Distribution field.
next to the Distribution field.
-
Choose Mapped field as the
Type, and click Continue.
-
In the Name text field, enter a name for the
mapped field. For information on naming objects, see
Using basic dialog box components.
In the Description text field, enter a description for the
mapped field.
-
Choose ODB mesh as the Data
source.
-
If desired, choose one of the following to enter a Scale
factor and to scale the source data coordinates; for example, to
account for a mismatch of units (i.e., meters to millimeters):
-
Choose Uniform, and enter a single scale
factor.
-
Choose Nonuniform, and enter a scale factor
for the X-, Y-, and
Z-coordinates.
-
Enter a value for Default unmapped field value,
or accept the default of zero.
Abaqus/CAE
assigns this value at any target points for which it cannot find a source point
from which to map. See
Search controls for mapped fields.
-
On the ODB Mesh Data tabbed page, select the
Viewport to map from the list of open viewports.
Abaqus/CAE
uses the current plot state of the selected viewport as the set of values to be
mapped onto the target model in your model database (.cae)
file; namely, the specific field output variable displayed at a specific step
and frame of the analysis.
-
On the Mapper Controls tabbed page, you can
adjust the search tolerance parameters. See
Search controls for mapped fields.
-
Click OK to create the mapped field and to
close the dialog box.
After you have created a mapped field using mesh-to-mesh mapping, you cannot
edit the source data mesh specifications; you can edit an existing mapped field
only to change the default field value or the mapper controls.
When you later apply a load, interaction, or predefined field using a mapped
field, you can display symbols in the viewport to visualize the locations and
magnitudes of the field values. However, you must mesh the model first to be
able to see these symbols.
 next to the
next to the