Creating the cube | ||
| ||
Context:
You then sketch its profile (0.04 m × 0.04 m) and extrude the profile over a specified distance (0.04 m) to produce the base feature of the first half of the hinge. The desired cube is shown in Figure 1.
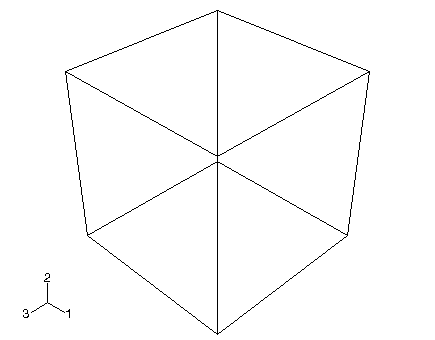
Note:
The default render style used throughout Abaqus/CAE is Shaded. For clarity, many of the figures in this tutorial use the wireframe or hidden line render styles. For more information, see Choosing a render style.
 .
.