Mirror your model
-
Locate the Mirror options.
From the main menu bar, select ViewODB Display Options. Click the Mirror/Pattern tab in the dialog box that appears. The Mirror options are in the upper portion of the page.
-
Accept the default global coordinate system, or select a coordinate
system from the Mirror CSYS list.
You can select any coordinate system that exists in the output database. If a suitable coordinate system does not already exist, you can create a new coordinate system using one of the methods described in Creating coordinate systems during postprocessing.
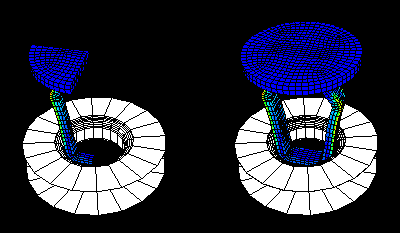
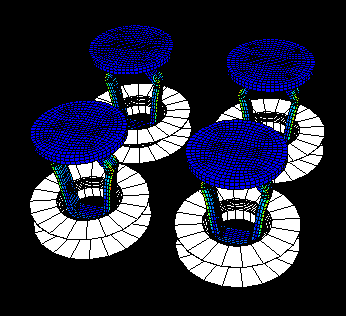
- Toggle on the mirror planes that you want Abaqus/CAE to use to copy the model results.
- Toggle on Mirror display bodies if you also want Abaqus/CAE to copy display bodies.
- If you apply mirrors in conjunction with rectangular or circular patterns, select the Order of Operations that Abaqus/CAE will use to create the copies.
-
Click Apply to implement your changes.
Your specifications are reflected in all plot states and are saved for the duration of the session. If you want to retain the changes you applied for subsequent sessions, save them to a file. For more information, see Saving customizations for use in subsequent sessions.
If a contour plot is displayed, the contours appear on all faces.
If a symbol or material orientation plot is displayed, the symbols or material orientations appear only on the original model faces.
 to determine the distance between the first and last
model nodes in the desired direction. (For more information, see
to determine the distance between the first and last
model nodes in the desired direction. (For more information, see