*CYCLIC | |||||||
|
| ||||||
ProductsAbaqus/StandardAbaqus/CAE
TypeHistory data
LevelStep
Abaqus/CAEInteraction module
Required parameters
- NC
-
Set this parameter equal to the number of cyclically similar images that compose the cavity formed as a result of this symmetry. The angle of rotation (about a point or an axis) used to create cyclically similar images is equal to 360°/NC.
- TYPE
-
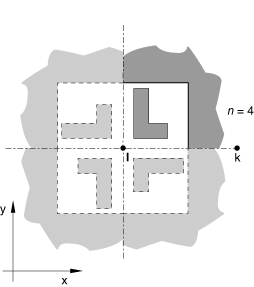
Set TYPE=POINT to create a two-dimensional cavity by cyclic repetition of the cavity surface defined in the model by rotation about a point, l. See Figure 1. The cavity surface defined in the model must be bounded by the line and a line passing through l at an angle, measured counterclockwise when looking into the plane of the model, of 360°/NC to .
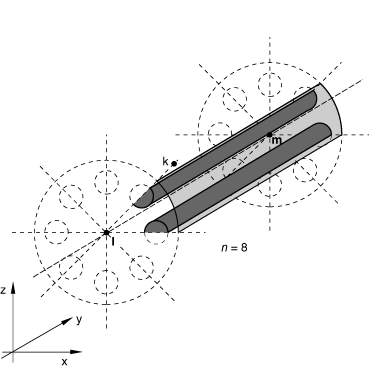
Set TYPE=AXIS to create a three-dimensional cavity by cyclic repetition of the cavity surface defined in the model by rotation about an axis, . See Figure 2. The cavity surface defined in the model must be bounded by the plane and a plane passing through line at an angle, measured clockwise when looking from l to m, of 360°/NC to . Line must be normal to line .
Data line to define cyclic symmetry for a two-dimensional cavity (TYPE=POINT)
- First (and only) line
x-coordinate of rotation point l (see Figure 1).
y-coordinate of rotation point l.
x-coordinate of point k.
y-coordinate of point k.
Data lines to define cyclic symmetry for a three-dimensional cavity (TYPE=AXIS)
- First line
x-coordinate of point l on rotation axis (see Figure 2).
y-coordinate of point l on rotation axis.
z-coordinate of point l on rotation axis.
x-coordinate of point m on rotation axis.
y-coordinate of point m on rotation axis.
z-coordinate of point m on rotation axis.
- Second line
x-coordinate of point k.
y-coordinate of point k.
z-coordinate of point k.