Introduction | ||
| ||
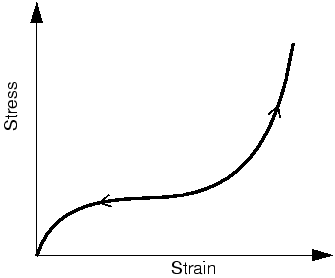
This type of material behavior is called hyperelasticity. The deformation of hyperelastic materials, such as rubber, remains elastic up to large strain values (often well over 100%).
Abaqus makes the following assumptions when modeling a hyperelastic material:
-
The material behavior is elastic.
-
The material behavior is initially isotropic.
-
The simulation will include nonlinear geometric effects.
In addition, Abaqus/Standard assumes the hyperelastic material is incompressible by default. Abaqus/Explicit assumes the material is nearly incompressible (Poisson's ratio is 0.475 by default).
Elastomeric foams are another class of highly nonlinear, elastic materials. They differ from rubber materials in that they have very compressible behavior when subjected to compressive loads. They are modeled with a separate material model in Abaqus and are not discussed in detail in this guide.