Specifying the offset of a conventional shell composite layup | ||
| ||
Context:
Positive values of the offset are in the positive element normal direction. When the offset is set equal to 0.5, the top surface of the element is the reference surface. When the offset is set equal to –0.5, the bottom surface is the reference surface. The default offset is 0, which indicates that the middle surface of the element is the reference surface. Figure 1 shows an offset to the top surface of the element.
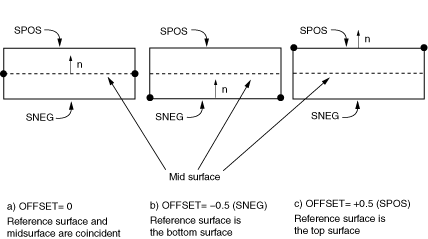
For more information, see Defining the Initial Geometry of Conventional Shell Elements. You can use a discrete field to model elements with continuously varying offsets. For more information, see The Discrete Field toolset.
 . For more information, see
. For more information, see