Modifying a sketch by dragging objects | |||||
|
| ||||
When you drag a vertex or an edge, Abaqus/CAE repositions the selection and uses the During drag constraint solution method to modify any connected edges (for more information, see Customizing the use of constraints in the Sketcher). Sketch constraints may cause multiple objects to move along with the one you select. Constraints may also restrict or prevent dragging some objects. For example, consider the sketch shown in Figure 1.
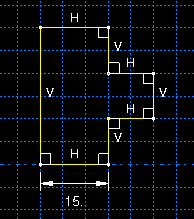
The sketch includes the default horizontal, vertical, and perpendicular constraints created by Abaqus/CAE during the sketching process and one added length dimension. With these constraints in place, dragging the left edge of the sketch has the same effect as dragging the vertex at either end of the left edge, as shown in Figure 2.
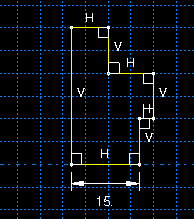
With the constraints and dimension removed, dragging the edge produces similar results to those shown in Figure 2, but dragging a vertex modifies the sketch as shown in Figure 3. The result in Figure 3 is achieved using the default Minimum move constraint solution method. For this sketch, dragging the vertex using any of the other constraint solution methods repositions the entire sketch.
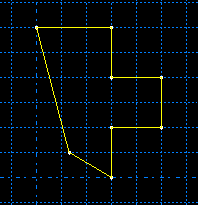
Dragging edges and vertices is a quick, but imprecise, method of moving them since the motion is based on the cursor position as opposed to an exact numerical change. To move objects more precisely, use the methods described in Modifying objects by changing dimensions or adding parameters, and Modifying or copying objects by selecting edges.
Dragging dimension text is one way to clean up the sketch after using the Auto-Dimension tool. The lack of precision does not matter since the exact location of dimension text is not important. When you drag dimension text, you can make the following changes:
-
Move a linear dimension closer to, farther from, or to the opposite side of the dimensioned quantity.
-
Move an angular dimension closer to or farther from the angle's vertex.
-
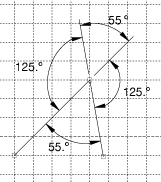
Move an angular dimension across one of the edges that define the angle to dimension a supplement of the original angle.
Possible locations for dragging an angular dimension are shown in Figure 4.
Dimension text is not controlled by any constraints other than the attachment to the dimensioned object. The constraint solution methods also do not affect dragging dimension text in a sketch.