Swept meshing of cylindrical solids | ||
| ||
Abaqus considers the following requirements for cylindrical elements when you attempt to mesh solid geometry with cylindrical elements:
The midside nodes on the circular edges of the cylindrical elements must be placed exactly halfway between the edge nodes.
All nodes on a cross-section must lie on the same radial plane.
All the circular edges within an element must span the same angle.
The centers of the circular arcs within an element must lie on a common axis.
An element cannot span more than 180°.
These requirements mean that you can create valid cylindrical elements only on revolved parts or parts that you can split into revolved domains. The S-shaped extrusion in Figure 1 can be meshed with cylindrical elements after partitioning into revolved regions.
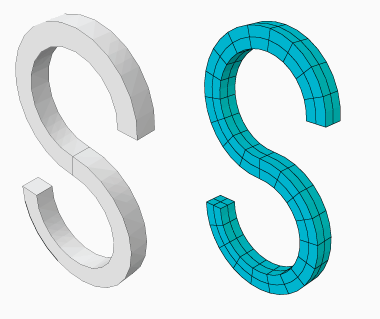
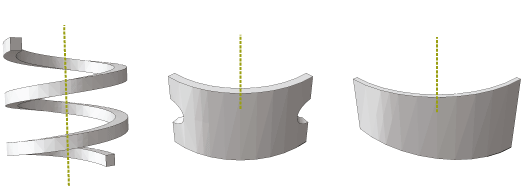
Figure 2 shows three types of geometry—a helical spring, a revolved part with cuts, and a tapered part—that cannot be meshed with solid cylindrical elements because of these meshing requirements.
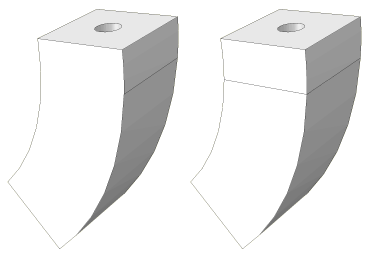
If one of the connecting sides that connect the source face to the target face in a revolved region is separated into multiple faces due to the internal edge or edges that constrain the mesh, the generated elements are likely to be too distorted to be used as cylindrical elements. You must partition the solid region into simpler revolved regions, as shown in the example on the right side of Figure 3.
When you edit a mesh part by assigning cylindrical elements to it, Abaqus/CAE considers Face 1 and Face 2 of each cylindrical element to be the faces along its radial planes. Figure 4 indicates the location of these faces for several types of cylindrical elements. You should orient the stack direction for elements in your part before assigning a cylindrical element type to it; for more information, see the descriptions in Orienting the stack direction.
