Mesh-geometry association | ||
| ||
Creating an association between orphan or bottom-up mesh entities (elements, element faces, element edges, and nodes) and adjacent geometry allows the transfer of loads, interactions, and boundary conditions from the geometry to the mesh. If you fully associate orphan or bottom-up mesh entities with an adjacent geometric face, you can use that face to create a native mesh for the geometry region that is compatible with the orphan or bottom-up mesh with which you started. Full association means that:
-
The selected geometric face is associated with element faces that cover the entire face.
-
All edges of the geometric face are associated with element edges that span the entire edge.
-
All vertices of the face are associated with nodes.
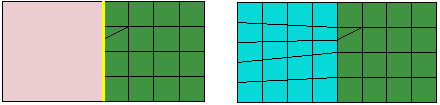
Figure 1 shows an example of the use of mesh-geometry association between a two-dimensional orphan element region and an adjoining geometric region. Associating the geometric edge—the yellow line in the left image—between the two regions with the orphan element edges and nodes results in a compatible hybrid mesh.
Conversely, if a model has a mesh that you need to preserve—because it includes extensive edits or is ideally suited to an analysis—and you do not want to make an orphan mesh for the entire part, you can delete the association between the mesh and selected entities to create orphan nodes and elements in selected regions. Deleting mesh associativity prevents Abaqus/CAE from deleting the mesh of a region when you edit the geometry. After making your edits, you can reestablish associativity between the geometric faces and the surface entities of the mesh. Nodes along edges are merged with any nodes that currently exist on the geometry.
If you delete the mesh-geometry associativity for a solid region, the only ways to reestablish a native mesh are to use the Undo function in the Edit Mesh dialog box or to assign the bottom-up mesh technique to the region and recreate the associativity.
The following rules apply to the association of bottom-up elements when you work with a region of solid geometry:
-
Abaqus/CAE always associates bottom-up elements with the selected region.
-
When the underlying geometry is used to define the shape of the mesh, Abaqus/CAE associates the mesh with that geometry.
-
When portions of the geometry are not used to define the bottom-up mesh, Abaqus/CAE does not associate them, even if the mesh and geometry are in the same location.
-
You can edit the mesh-geometry association of any geometry-based bottom-up meshed region.
-
Even if you edit a generated mesh so that it matches the geometry, you must still manually associate the mesh with the geometry.
There are three considerations that make mesh-geometry association critical to creating a good analysis model:
-
When you work with geometry, attributes such as loads and boundary conditions are applied to the geometry. Proper mesh-geometry association ensures that these attributes are transferred correctly to the mesh during the analysis.
-
If you select a geometric face as a source or connecting side of a bottom-up mesh, Abaqus reuses the existing mesh entities on that face to create a compatible mesh only if the mesh entities are fully associated with the selected face.
-
Abaqus tries to merge meshes that are associated with the same geometric entities. Unassociated meshes may require you to merge nodes along mesh boundaries using the Edit Mesh toolset.
You should always check that the mesh-geometry associativity is correct when working with bottom-up meshes or editing the associativity of any mesh. Abaqus/CAE will issue an error in the Job module if you submit a job and attributes are applied to geometry with no associated mesh. However, Abaqus/CAE cannot determine whether the association is correct. For example, if a load is applied to a geometric face that should have several hundred elements but only one element is associated with that face, Abaqus/CAE will attempt to analyze the model with the entire load applied at the single associated element. Incorrect association produces incorrect analysis results.
You can use the mesh-geometry association
 and delete mesh associativity
and delete mesh associativity
 tools in the
Mesh module
toolbox to view and edit or to delete mesh-geometry associations. For detailed
instructions, see
Viewing and editing mesh-geometry associativity
and
Deleting mesh-geometry associativity.
tools in the
Mesh module
toolbox to view and edit or to delete mesh-geometry associations. For detailed
instructions, see
Viewing and editing mesh-geometry associativity
and
Deleting mesh-geometry associativity.