Problem description
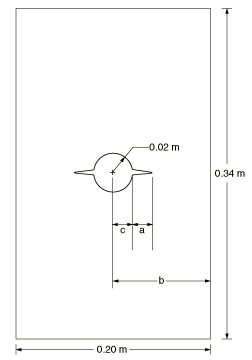
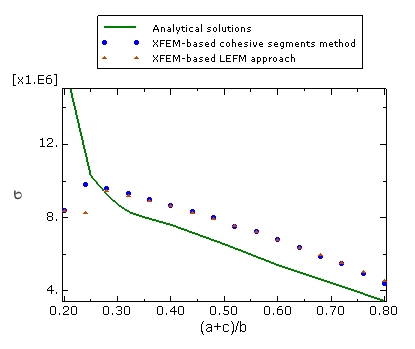
A plate with a circular hole is studied. The specimen, shown in Figure 1, has a length of 0.34 m, a thickness of 0.02 m, a width of 0.2 m, and a hole radius of 0.02 m, under pure Mode I loading. Figure 1 defines the dimensions used to calculate the variation of crack length, : a is the crack length, b is half the specimen width, and c is the hole radius.
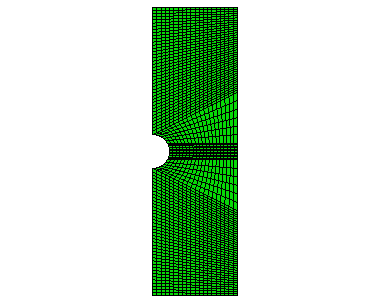
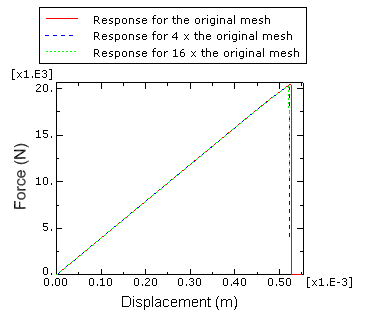
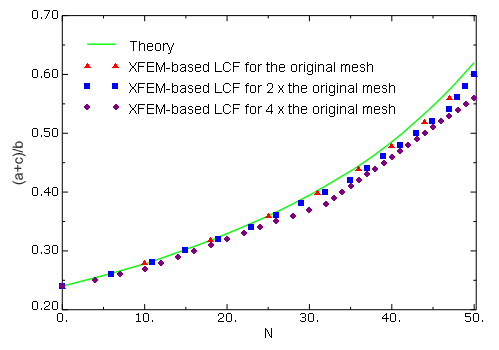
Equal and opposite displacements are applied at both ends in the longitudinal direction. The maximum displacement value is set equal to 0.00055 m. To examine the mesh sensitivity, three different mesh discretizations of the same geometry are studied. Symmetry conditions reduce the specimen to a half model. The original mesh, as depicted in Figure 2, has 2060 plane strain elements. The second mesh has four times as many elements as the original one, while the third mesh has sixteen times as many elements as the original one.
In the low-cycle fatigue analysis, two steps are involved. A static step is used to nucleate a crack at the site of stress concentration prior to the low-cycle fatigue direct cyclic step, in which a cyclic distributed loading with a peak value of 1.25 MPa is specified. Three different mesh discretizations of the same geometry are studied. The second mesh has twice as many elements as the original mesh, while the third mesh has four times as many elements as the original mesh.
The material data for the bulk material properties in the enriched elements are GPa and = 0.3.
The response of cohesive behavior in the enriched elements in the model is specified. The maximum principal stress failure criterion is selected for damage initiation, and an energy-based damage evolution law based on a BK law criterion is selected for damage propagation. The relevant material data are as follows: MPa, × 103 N/m, × 103 N/m, and . The relevant material data defined above are also used in the model simulated using the XFEM-based LEFM approach. When the low-cycle fatigue analysis using the Paris law is performed, the additional relevant data are as follows: , , × 10−6, , , and .