About the Model
In this model, a clustered plate is encastered on the left side
with a load of L = 100 N in the negative Y-direction on the right side. The plate is also
fixed in Z-direction to prevent (for example, out of plane buckling motion).
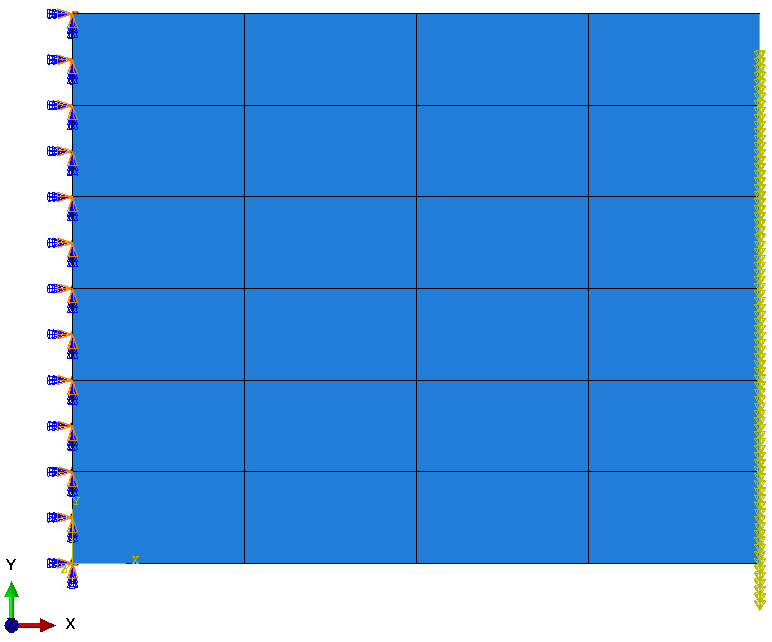
In this example, it will be shown how differences between elastic and elastic-plastic
material affect the optimization results. The sizing optimization task is to minimize the
volume of the plate while using von Mises stress constraints. By default, the shell
thicknesses are allowed to change up to 25% of the initial thickness and are changed for
each element cluster. Within a cluster, the elements will have the same thickness.
Procedure Summary
| Model: |
Plastic_Plate, Elastic_Plate |
| Design Area: |
All elements |
| Objective: |
Minimize volume |
| Constraint: |
von Mises stress less or equal 425 MPa (slightly above yielding point) |
See Also
A detailed explanation of the effects of geometric nonlinearities can be found in the
SIMULIA Tosca Structure User Guide (see
Effects of Nonlinear Material Laws).
