Effects of Nonlinear Material Laws | ||
| ||
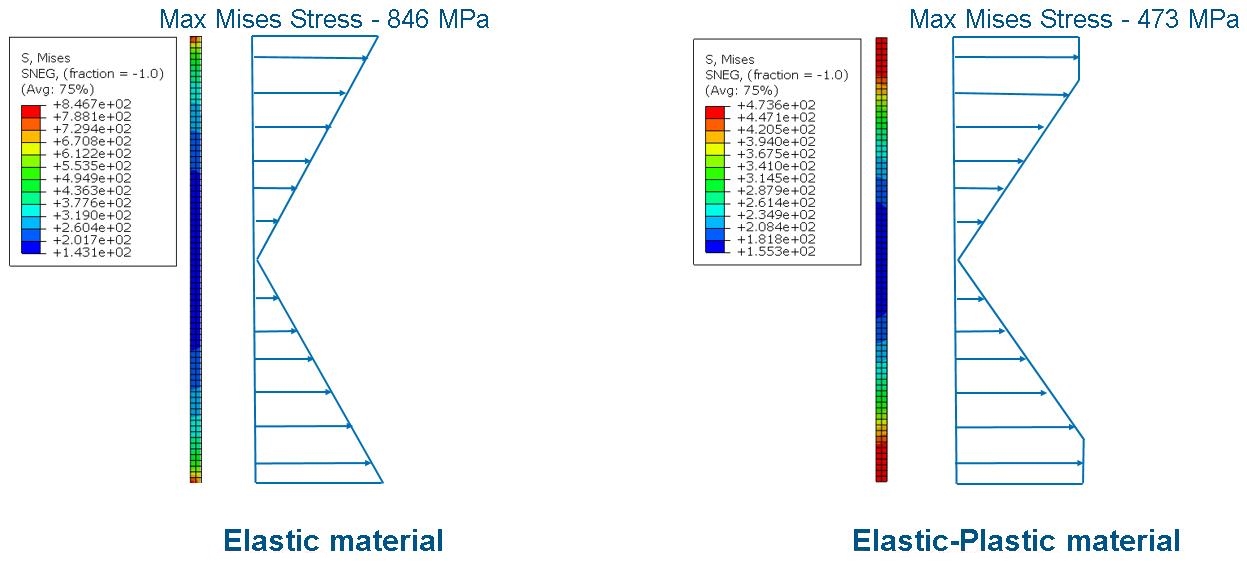
Elastic-Plastic Material with a Bending Plate
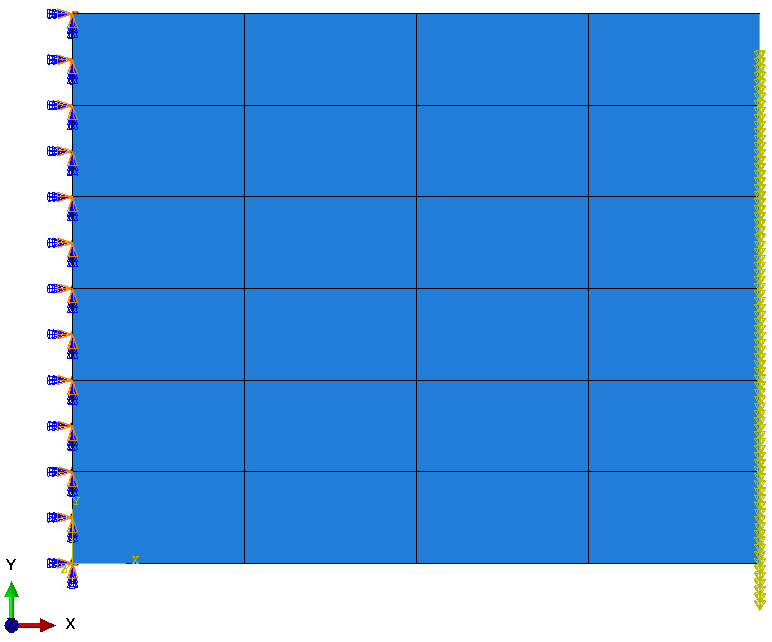
A vertical plate has one edge encastered and the opposite edge subjected to a load F in the negative Y-direction. In two scenarios, the material is chosen to be elastic and elastic-plastic, respectively. In the elastic material, the maximum stress occurs at the two encastered corners, while in the elastic-plastic material the effect of yielding increases the region of maximum stress across an envelope around the encastered corners. Seen in the graphic below.
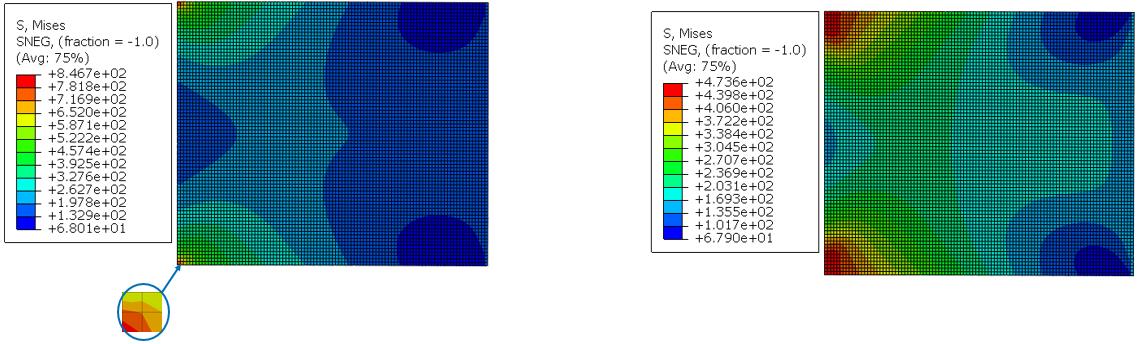
By taking a thin strip from the left side of the plate, it can be sees that with elastic-plastic material the stresses are leveled in the outer regions (below, right side). This is because of the yielding effect where stress does not increase with increasing strain. On the contrary with elastic material, the stresses scale linearly across the plate and reach higher values at the boundaries.