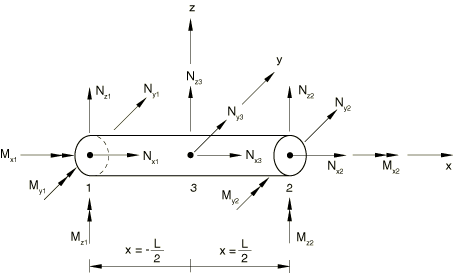
The elastic response of the element is governed by Euler-Bernoulli beam
theory. The displacement interpolation for the deflections transverse to the
frame element axis (the y- and
z-directions) uses fourth-order polynomials, allowing for
quadratic variation of the curvature along the beam axis. Let
be the isoparametric coordinate along the length of the beam. Then,
The transverse displacement interpolations incorporate exact solutions to
force and moment loading at the ends and constant distributed loads along the
beam axis (such as gravity loading). The displacement interpolation function
along the frame element axis (the x-direction) is a
second-order polynomial, allowing for linear variation of the axial strain
along the frame element axis:
The twist rotation degree of freedom interpolation along the beam axis
(rotation about the x-axis) is linear, allowing for
constant twist strain:
The generalized strains, following Euler-Bernoulli beam theory, are
where
is the axial strain,
and
are the beam curvatures, and
is the twist strain. The 15 undetermined constants in the interpolation
equations for the displacements are determined by introducing the nodal degrees
of freedom; that is,
The interpolations in terms of the nodal degrees of freedom are described
below in the section discussing the large-displacement formulation.
The strain-displacement relationship is written in matrix form as
where
is a 4
15 matrix and
The elastic stiffness matrix is integrated numerically and used to calculate
15 nodal forces and moments—12 forces/moments (also called generalized forces)
associated with the two end nodes,
and three forces associated with the internal node,
The vector of forces and moments for the frame element can be written as
The elastic stiffness is, therefore, a
matrix relating the force vector, ,
and the nodal displacement vector, :
Material properties of frame elements can, in general, be temperature
dependent. Let us define the elastic strain vector as
where
denotes the total strain and
denotes the thermal expansion strain, where only the axial strain is nonzero
and is given by
where
is the thermal expansion coefficient,
is the current temperature at the frame element section,
is the reference temperature for ,
and
is the user-defined initial temperature at this point (Initial Conditions).
The temperature field is defined by the user at the element's ends and is
assumed to be linear along the element axis but constant within the element
cross-section. If the thermal expansion coefficient is temperature dependent,
it is evaluated at the nodes. Thermal strains are calculated at the element's
end nodes, and thermal strains at the integration points are interpolated from
the nodal points using appropriate interpolation schemes: axial strains are
interpolated linearly, curvatures are interpolated quadratically, and twist
strain is constant along the frame element axis.
Initial generalized strains, ,
are calculated from the initial generalized forces given by the user, using the
relationship
where
denotes the
material matrix evaluated at the nodal temperature :
and A is the cross-section area; E
is Young's modulus; G is the shear modulus;
,
,
and
are cross-section moments of inertia; and
is the torsional stiffness. The vector of generalized initial forces includes
the following components:
Initial strains, when needed, are interpolated from the nodal values to the
integration points using appropriate interpolators: linear for the axial
component, quadratic for the bending components, and constant for the torsional
component.
Abaqus
integrates the elastic stiffness matrix numerically:
where temperature-dependent material properties are evaluated at the
integration points, assuming a linear variation of temperature along the
element axis.
For the simplest case of a temperature-independent material and a pipe
cross-section, the elastic stiffness matrix can be integrated analytically to
give:
Twisting moments at the end nodes:
Axial forces at the nodes:
Bending moments at the end nodes and transverse forces for all three nodes:
where
is the bending part of the elastic stiffness matrix and takes the following
form: