Link and Coupling Conditions Overview | ||||||
|
| |||||
- In Tosca Structure.gui, select .
Each link condition has a name (ID_NAME parameter).
A criterion for determining the main node (MAIN
parameter) is defined as well as a rule for the displacement of the client
nodes (CLIENT parameter).
A typical LINK_SHAPE
command appears as follows:
LINK_SHAPE
ID_NAME = name_of_link_shape
MAIN = ...
CLIENT = ...
...
END_
Depending on the selected CLIENT parameter, other parameters are also
required. In some circumstances, a coordinate system (CS parameter) or
tolerances (TOL parameter) must be specified. These parameters of a
LINK_SHAPE command might appear as follows:
LINK_SHAPE
...
CS = name_of_coord_system
TOL = <tol_1>, <tol_2>, <tol_3>
END_
In the following subsections, the MAIN and CLIENT
parameters are described in detail. The CS and TOL
parameters are also described when applicable.
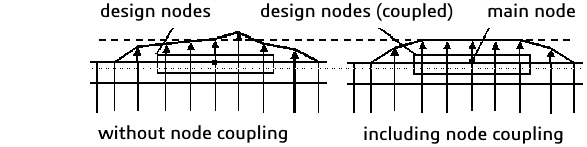 |
Link conditions basically only define a coupling rule without referencing
a specific node group. The coupling condition is assigned to a node group
after activation with CHECK_LINK in the DVCON_SHAPE
command.
- In Tosca Structure.gui, the link condition is assigned in the menu of the DVCON_SHAPE command.
| Important:
|
Determining the Main Node (MAIN)
The MAIN parameter is used in each definition of
a link condition to specify how to determine the main node. This node
prescribes the displacement of the nodes affected by the link condition.
It can be set explicitly by the user:
MAIN = NODE, node_nr
This causes the main displacement to be determined from the same node during the entire optimization.
In addition, the main node might be determined from a main node group. This allows the user to define a components edge to be the main edge for optimization. The algorithm determines the main node automatically from the main node group. In this case, the main node group must contain exactly one node of each link group.
MAIN = NDGR, <nodegroup>
Another way is to have the system automatically determine the main node according to two different criteria:
MAIN = MAX
or
MAIN = MIN
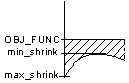
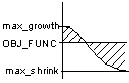
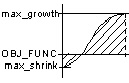
In this case, the main node is redetermined in every cycle. When the main node is automatically determined, the critical factor is identifying which node displacement (determined by the stress) for the coupling group is relevant. Principally, there exist four different cases of how the largest and smallest node displacements relate to the reference value within the node group:
- Case 1: The stress everywhere is greater than the reference value; a positive displacement is determined for all design nodes of the coupling group. All design nodes grow out of the component.
- Case 2: The stress everywhere is less than the reference value; for all design nodes of the coupling group a negative displacement is determined. All design nodes shrink inwards.
- Case 3: There are nodes with greater and less stress than the reference value and the absolute shrinkage is greater than the absolute growth (abs(max_neg) > abs(max_pos)).
- Case 4: There are nodes with greater and less stress than the reference value and the absolute shrinkage is less than the absolute growth (abs(max_neg) < abs(max_pos)).
Case 1 |
Case 2 |
Case 3 |
Case 4 |
|
ALL_GROWTH |
ALL_SHRINK |
MORE_SHRINK |
MORE_GROWTH |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
lab1 = |
Selected Main Displacement Value |
|||
MAX |
max_growth |
min_shrink |
max_growth |
max_growth |
MIN |
min_growth |
max_shrink |
max_shrink |
max_shrink |
The two criteria MAX and MIN, respectively,
select different main nodes corresponding to the selected displacement
values:
MAX: TheMAX-Criterion is theconservativeoption. Here, the maximum growth (as in the cases 1, 3, 4) or the smallest shrinkage (as in case 2) is always used to select the main node. This is the standard criterion for shape optimization.MIN: TheMINcriterion moves the component surface inward as far as possible. This criterion must be used when linking conditions are required while optimizing contact surfaces.
CHECK_LINKin theDVCON_SHAPEcommand assigns the link condition to a node group. ForMAIN=NODE,node_nr, the explicitly declared node must not necessarily be contained in the node group. ForMAIN=MAXorMAIN= MIN, the main node is always determined from the nodes of the node group.- Older parameters
CRIT_1andCRIT_2correspond toMAXandMINrespectively. With Tosca Structure 2023, these older definitions are still supported.
Displacement of the Client Nodes (CLIENT)
The CLIENT parameter
is used in each definition of a link condition to set a rule for determining
the displacement of the client nodes based on the displacement of the
main node. The client nodes are moved relative to the main node.
The following rules can be selected:
- Plane Symmetry (PLANE_SYM)
- Plane Symmetry for Nonsymmetric Meshes (SURF_PLANE_SYM)
- Cyclic Symmetry for Nonsymmetric Meshes (SURF_CYCLIC_SYM)
- Cyclic-Plane Symmetry Combination (SURF_CYCLIC_PLANE_SYM)
- Point Symmetry (POINT_SYM)
- Rotational Symmetry (ROTATION_SYM)
- Coupling Displacement Coordinates (VECTOR)
- Coupling Displacement Direction (DIRECTION)
- Coupling Amount of Displacement (LENGTH)
- Coupling Coordinates in the FE Displacement Coordinate System (DISP_CS)
- Stampable Surface (SURF_STAMP) for Shape Controller
- Turnable Surface (SURF_TURN) for Shape Controller
- Turnable Surface (SURF_TURN) for Shape Sensitivity
- Drillable Surface (SURF_DRILL)
- Demoldable Surface (SURF_DEMOLD)
- Restricting Displacement to a Slide Surface(
FREE_FORM)
The individual rules for determining the client displacements are described in detail in the linked chapters.
Not all link conditions are applicable for both, the controller and the sensitivity-based shape optimization approach. The table below shows which types are usable with which approach.
| CLIENT / Applicable for | SHAPE_CONTROLLER | SHAPE_SENSITIVITY |
|---|---|---|
| PLANE_SYM | OK | - |
| SURF_PLANE_SYM | OK | OK |
| SURF_CYCLIC_SYM | OK | OK |
| SURF_CYCLIC_PLANE_SYM | OK | OK |
| POINT_SYM | OK | - |
| ROTATIONAL_SYM | OK | - |
| VECTOR | OK | - |
| DIRECTION | OK | - |
| LENGTH | OK | - |
| DISP_CS | OK | - |
| SURF_STAMP | OK | OK |
| SURF_TURN | OK | OK |
| SURF_DRILL | OK | - |
| SURF_DEMOLD | OK | OK |
| FREE_FORM | OK | - |
Example: Link Condition with Fixed Main Node
All nodes of the previously defined node group node_rigid
should have the same displacement with respect to the global Cartesian
coordinate system as the design node with the number 46. Node 46 need
not be a part of the node group node_rigid. The link
condition should have the name link_rigid. The link
condition is then used in the restriction with the name dvcon_rigid.
LINK_SHAPE
ID_NAME = link_rigid
MAIN = NODE, 46
CLIENT = VECTOR
CS = CS_0
END_
DVCON_SHAPE
ID_NAME = dvcon_rigid
ND_GROUP = node_rigid
CHECK_LINK = link_rigid
END_
Example: Coupling Condition with Automatic Determination of the Main Node
All nodes of the node group ndgr_left should have
the same displacement as the node from ndgr_left that
has the greatest outward displacement. In the same way, all nodes of
the node group ndgr_right should have the same displacement
as the node from ndgr_right that has the greatest outward
displacement. This requires a link condition and two restrictions.
LINK_SHAPE
ID_NAME = link_left_or_right
MAIN = MAX
CLIENT = VECTOR
CS = CS_0
END_
DVCON_SHAPE
ID_NAME = dvcon_left
ND_GROUP = ndgr_left
CHECK_LINK = link_left_or_right
END_
DVCON_SHAPE
ID_NAME = dvcon_right
ND_GROUP = ndgr_right
CHECK_LINK = link_left_or_right
END_
In each design cycle the system identifies which nodes in each of the
node groups, ndgr_left and ndgr_right,
has the greatest positive displacement (in the growth direction). Usually,
these are the nodes with the largest stress difference between the effective
value and the targeted value. These displacements are then applied to
all nodes of the node groups ndgr_left and ndgr_right,
respectively. The following command can be used instead of the two individual
DVCON_SHAPE commands:
DVCON_AUTO_SHAPE
ID_NAME = dvcon_*
ND_GROUP_FAMILY = ndgr_*
CHECK_LINK = link_left_or_right
END_
The naming left and right is determined
automatically from the complete name of the node groups and added to
the root name of the automatically generated DVCON_SHAPE
entries. However, this requires that only these two node groups begin
with the name ndgr_ otherwise other node groups are
taken into consideration.