About the Clip Example | ||
| ||
About the Model
The maximum stress is found on the inner side of the clip.
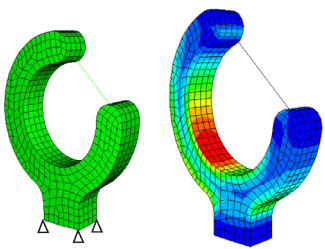
The aim of optimization is to reduce the stresses without changing the contour of the inner side. Only nodes on the outer side are to be designed. The stress level is very low at the tips. Therefore, an optimization without restrictions would result in these low-stressed areas shrinking. Thus, two cylindrical frozen areas are defined at the tips.
Procedure Summary
| Model: | clip.ext |
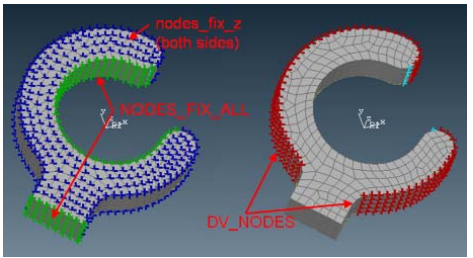
| Design Area: | Node group DV_NODES |
| CS_DEF | New rectangular coordinate system, defined by rotating the global CS by 45° around the global z-axis |
| CS_DEF | New cylindrical coordinate system, defined by translating the previously defined rectangular CS to origin with coordinates (23,23,0) |
| CS_DEF | New cylindrical coordinate system, defined by translating the previously defined rectangular CS to origin with coordinates (23,-23,0) |
| Design Variable Constraint: | Two solid body boundaries for the design nodes |
| Design Variable Constraint: | Fixation of all displacements for the node group NODES_FIX_ALL |
| Design Variable Constraint: | Fixation of the displacement along the global z-axis for the node group nodes_fix_z |
| Design Variable Constraint: | Maximal growth and shrinkage of 6 mm for the design nodes |
| Mesh Smooth: | Mesh smoothing of all elements, while free surface nodes remain free |
| Objective: | Minimize the maximal von Mises stresses in the design area |
| Stop Condition | The global stop condition is set to 5 iterations |