ACCELEROMETER | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
ProductsAbaqus/ExplicitAbaqus/CAE
Description
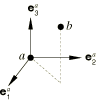
The ACCELEROMETER connection does not impose kinematic constraints. It defines three local directions at node a and three local directions at node b. The ACCELEROMETER connection's formulation is similar to that for the CARTESIAN connection. The ACCELEROMETER connection measures the position of node b relative to node a
The coordinate system at node b rotates with the rotation of node b, and the kinematic quantities are reported in this rotated coordinate system as shown in Figure 2.
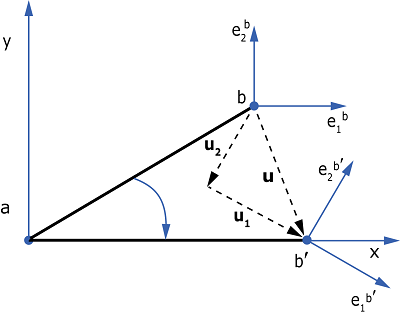
There are no available components of relative motion for the ACCELEROMETER connection. The connector displacement components are
where , , and are the initial coordinates of node b relative to node a.
The ACCELEROMETER connection measures velocity and acceleration in the local directions at node a as if node a were an inertial frame. In contrast to the CARTESIAN connection, the ACCELEROMETER connection reports all the computed quantities (such as displacement, position, velocity, and acceleration) in the local directions at node b. Let be the transformation from to . Then the ACCELEROMETER connection measures velocity and acceleration as
where the derivatives above are time derivatives in a system moving with .
In two-dimensional and axisymmetric analyses .
Summary
| ACCELEROMETER | |
|---|---|
| Basic, assembled, or complex: | Basic |
| Kinematic constraints: | None |
| Constraint force output: | None |
| Available components: | None |
| Kinetic force output: | None |
| Orientation at a: | Optional |
| Orientation at b: | Optional |
| Connector stops: | None |
| Constitutive reference lengths: | None |
| Predefined friction parameters: | None |
| Contact force for predefined friction: | None |