Using discrete orientations for material orientations and composite layup orientations | |||||||
|
| ||||||
Context:
A variety of selection methods are available to define the desired axes. The datum axis and vector value methods define a constant axis direction, whereas the region selection methods allow for varying orientations. For example, you may want to select a curved surface and allow the normal to follow the shape of the curve.
Abaqus/CAE uses the normal axis and primary axis that you specify and the following algorithm to calculate the discrete orientation:
Abaqus/CAE preserves the normal axis direction and uses the specified primary axis direction as a construction direction. If the specified primary axis direction and the normal axis direction form a 90° angle, the final primary axis direction will be the same as the one specified. Otherwise, the primary axis direction will be adjusted to form a Cartesian system.
If you define the normal axis by selecting a surface or face, Abaqus/CAE finds the closest point on the surface or face and uses the surface normal at that point as the normal axis direction ().
If you define the primary axis by selecting an edge, Abaqus/CAE finds the closest point on the edge and uses the edge tangent at that point as the primary axis construction direction ().
Abaqus/CAE computes the secondary axis direction () by taking the cross product of the primary axis direction and the normal axis direction ().
Abaqus/CAE computes the final primary axis direction () by taking the cross product of the secondary axis direction and the normal axis direction ().
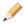 .
. .
. and select two points in the viewport that define the axis.
and select two points in the viewport that define the axis. to obtain the desired direction.
to obtain the desired direction.