About Array Parameters | |||||
|
| ||||
When you use array parameters in calculations, you must consider the following:
-
Array functions do not support array slices. You must use either a single element of the array or the entire array.
-
An array can be used as an argument to any operator or function. The operator or function is applied to each element of the array and an array of the same size is returned. If multiple arrays are used as arguments, they must all be the same size and shape. For example, to normalize all elements of an array, enter the following:
dy = dy - mean(dy)In the following figure an array parameter called
dyis used in a calculation: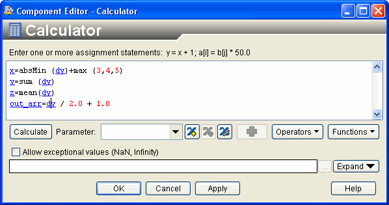
-
You can pass only one array parameter to a statistical function, such as
sum(dy). You can pass multiple scalar variables, such as . -
Only arrays of numeric datatype (real, integer) are available for use in calculations.
-
If you are working with a resizable array and you assign an array element that is beyond the end of the array, the array expands. For example, if array
arrhas 5 elements and you execute the calculation:i=6 arr[i]=99
then
arrexpands to size 7 (elements 0 through 6) when the second statement executes. Non-resizable arrays are resized by the Calculator Component Editor when they are used with constants as the subscripts, but they are not resized at run time. -
The following statistical functions have special behavior when they pass one array as an argument. Instead of acting separately on each element of the array, the functions build a single result from the values of all array elements. These functions can take a 1D vector or a 2D matrix (or higher dimensional array). All array elements are processed as if the whole array was flattened to a single vector.
sum
Sum of all elements of the array.
min
Minimum value of all elements in the array.
max
Maximum value of all elements in the array.
mean
Mean value of all elements in the array.
stddev
Standard deviation of all array elements from the mean.
absSum
Sum of the absolute values of all elements in the array.
absMax
Maximum of the absolute values of all elements in the array.
absMin
Minimum of the absolute values of all elements in the array.
-
The following functions also take an array as an argument and return information about that array:
maxIdx
Index of the maximum value in a 1D array.
minIdx
Index of the minimum value in a 1D array.
absmaxIdx
Index of the maximum absolute value in a 1D array.
absminIdx
Index of the minimum absolute value in a 1D array.
size
Returns the total number of elements in the array. Works for single and multi-dimensional arrays.
dim (array, dimension)
Returns the size of a single dimension of a multi-dimensional array. Dimensions are counted starting at 1, so
dim(table, 1) is the number of rows, anddim(table, 2) is the number of columns.