About Determining the Point of Program Termination | ||
| ||
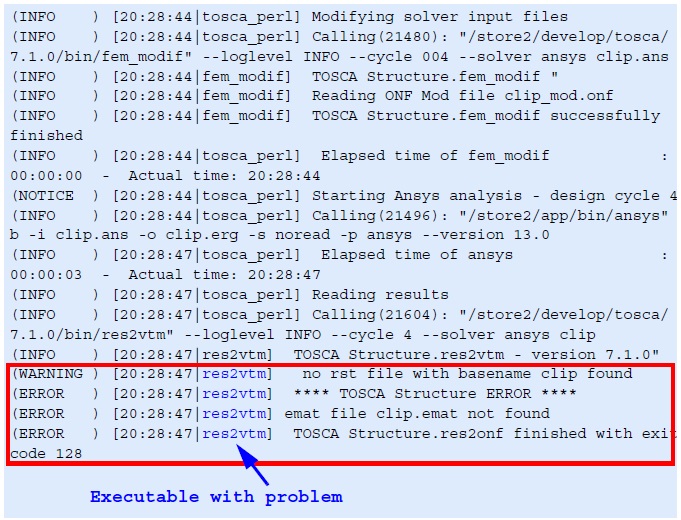
Trouble shooting in TOSCA.OUT. Here, the result reader
RES_2_VTM stops because of missing results files. The reason for
this error can be found in the logfiles of the FE-solver that has terminated
incorrectly.
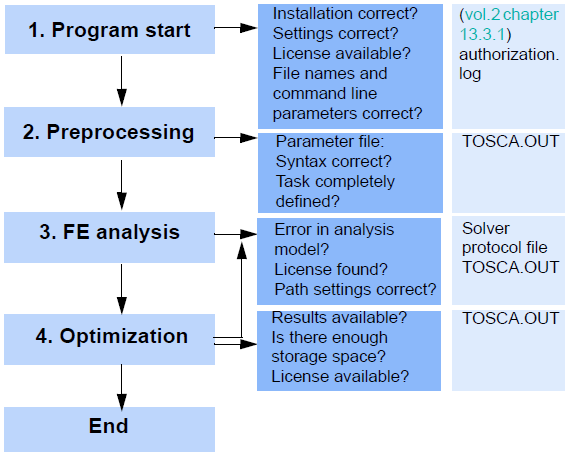
The following four points of the optimization process are known to be the most frequent in which an error might occur:
- Stop at the start of the program (configuration, licensing, and control start).
- Stop in a preprocessing step (
FEM_INCLUDE, FEM_2_ONF, TOSCA_PREP). - Stop during a FE analysis.
- Stop in an optimization step (
RES2VTM, TOSCA_OPT, FEM_MODIF).
For a more detailed description of the program sequence, see the figure in Program Sequence and Data Flow of Tosca Structure. When the program is started, the configuration is first loaded and the licenses are checked. Information regarding this can be found in the protocol file authorization.log (see also Special Logfiles).
Afterwards, the Tosca Structure
control program will be started. Protocol information will be printed
to the display and to the file TOSCA.OUT.

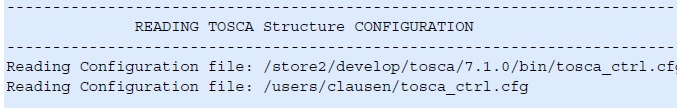
The sequence of configuration
files that are read in the beginning of the optimization will be logged
to TOSCA.OUT:
For each module that
is started by the control program and finishes, an entry with information
concerning the running time of the module can be found. For example,
in TOSCA.OUT in the fourth iteration:
The course of the
individual processes and cycles can be seen in the following figure and can be followed in the protocol file TOSCA.OUT.
Several points should be checked depending on where the program stop occurred. These are illustrated in the diagram below together with the protocol files where the error messages are saved. Different error messages, their causes, and possible ways of correcting these errors are also described in the following section. A description of which files contain error messages is also given.