Effects of Geometric Nonlinearities | ||
| ||
Nonlinear Geometry with a Bending Plate
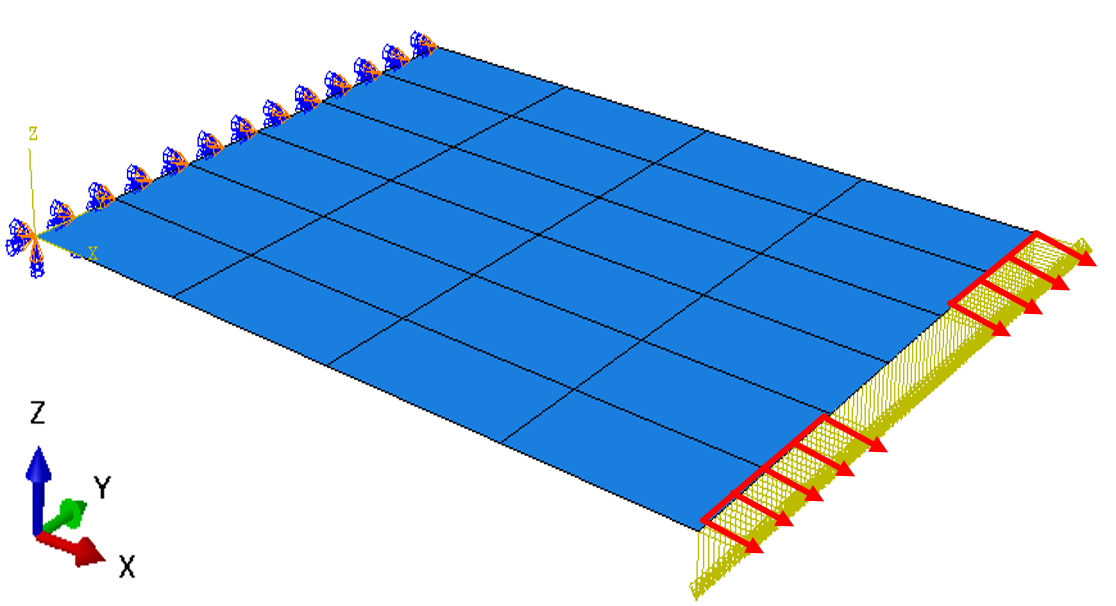
A horizontal plate has one edge encastered and the opposite edge subjected to a force in negative Z-direction as well as a force in positive X-direction where >> . When taking only linear kinematics into account, the displacement of the loaded edge is only in the negative Z-direction because of the load in Z and superposed with the displacement in X causes by the X-load. Thus, the membrane load in X only contributes to the total displacement in X: = . The plate elongates, which the graphic below shows (right side):
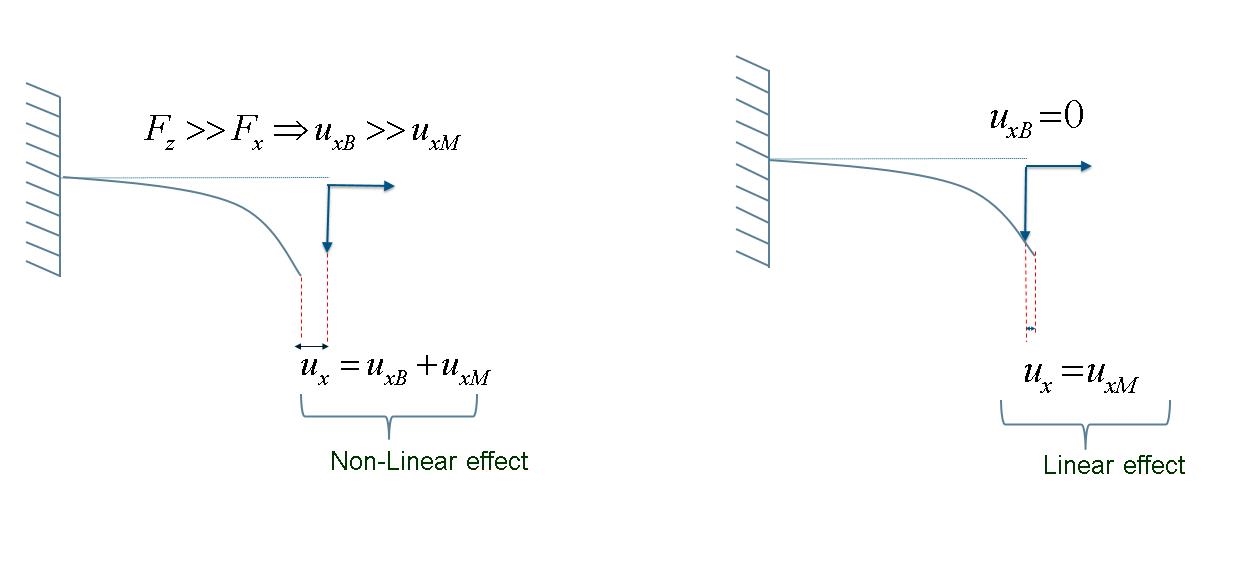
. By taking geometric nonlinearities into account (NLGEOM=YES), there is an additional displacement in the negative X-direction due to the bending movement of the plate. Thus, the total displacement of the right edge is the sum of displacement because of the loads in X and Z, respectively. In this example, the bending load in Z is larger than the tensile force in X. This leads to a high bending displacement and the total displacement = + is negative, which can be seen in the graphic above (left side).